Sep 1, 2023
Objectives – Exploring Einstein AI and Advanced Analytics
This chapter will focus on the concept of advanced analytics and its applications in Tableau and Salesforce. The chapter will begin by defining advanced analytics and its capabilities in providing deeper insights and predictions from data. The chapter will then cover the use of advanced analytics in Tableau, highlighting relevant features. Additionally, the chapter will delve into advanced analytics in Salesforce, including its Einstein platform and its capabilities for machine learning and AI-powered insights. Lastly, the chapter will guide how to create a combined analytical use case across Tableau and Salesforce, leveraging the strengths of both platforms for enhanced data analysis and decision-making.
The chapter covers the following topics:
- Advanced analytics
- Using advanced analytics in Tableau
- Using advanced analytics in Salesforce
- Combining Tableau and Salesforce for advanced Analytics
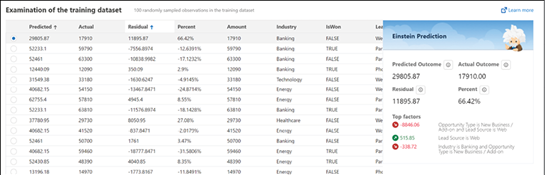
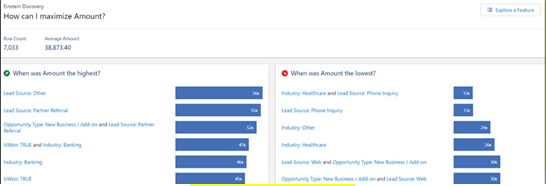
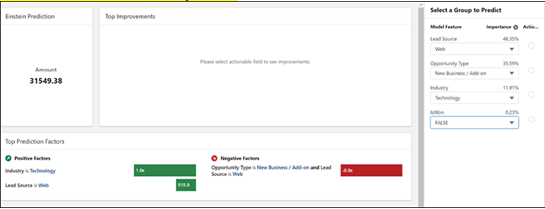
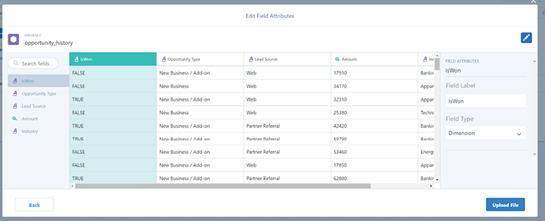
This chapter provides learners with a comprehensive understanding of advanced analytics and its significant role in interpreting data and aiding decision-making. It explores the potential of advanced analytics to yield deeper insights and more accurate predictions. Learners will discover how to harness the capabilities of advanced analytics in Tableau, leading to robust data visualization and exploration. The chapter also imparts knowledge about Salesforce’s Einstein platform, which incorporates machine learning and artificial intelligence to facilitate advanced analytics. Additionally, it explains how Salesforce utilizes advanced analytics to enhance customer relationship management and other business functions.
A key focus of the chapter is teaching learners how to create a combined analytical use case that leverages the strengths of both Tableau and Salesforce for improved data analysis. This involves understanding the integration and synergies between these platforms, which is crucial for optimizing their use in a business context. Finally, learners are encouraged to apply the techniques and knowledge acquired to real-world problems. This application not only enhances their data analysis skills but also bolsters their strategic decision-making capabilities, equipping them with the tools to make informed, data-driven decisions in various business scenarios.
More Details