Jul 12, 2024
Tableau and Salesforce: a powerful combination– Troubleshooting, Tricks, and Best Practices
In the previous chapters, we delved into the incredible power the combination of Salesforce and Tableau offers to organizations. By pulling together these world-class solutions, businesses can not only access a wide array of features but also unlock unique synergies that boost their operational efficiency and decision-making prowess.
Let us take a moment to reflect on the insights we have gathered so far.
Tableau’s advanced visualization tools make the wealth of data stored in Salesforce readily understandable and actionable. By crafting intuitive dashboards, teams across your organization can leverage Salesforce’s rich customer data to gain insights previously hidden in the complexity of raw data. Merging Salesforce data with information from other business sources also allows for a more holistic view of your business and its customers, enabling you to make decisions with confidence and precision.
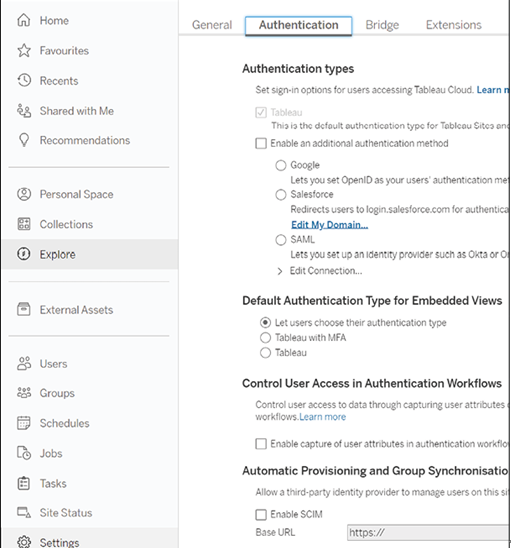
We also discussed how bringing Tableau dashboards into the Salesforce CRM environment enhances user efficiency. Having visualized data within the same workspace where business activities take place saves precious time and prevents potential information loss that can occur during context switching. The power of Tableau’s Dashboard Starters and the seamless integration within Salesforce CRM workflows translate into convenience and deeper understanding, equipping your teams with the tools to make smarter, more informed decisions.
We delved into the fascinating world of Einstein AI and how its advanced insights can propel your Tableau dashboards to another level. Einstein AI’s easy-to-set-up models connect your analytics to actionable next steps. Coupled with Data Cloud for Tableau, this enables your organization to tap into unified data sources, providing a wide field of view of your customer’s journey.
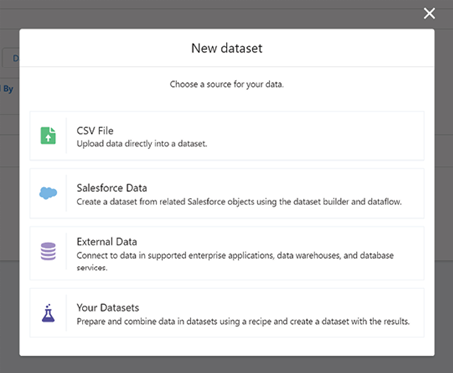
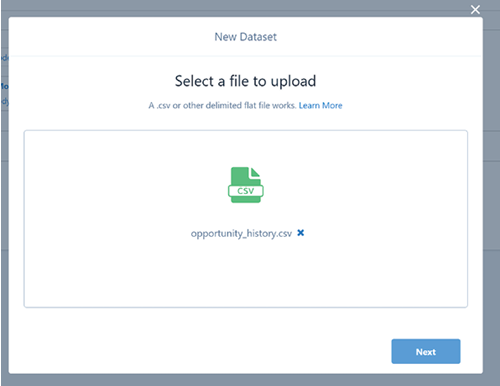
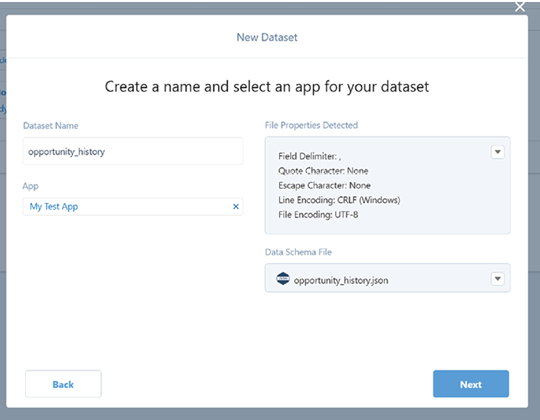
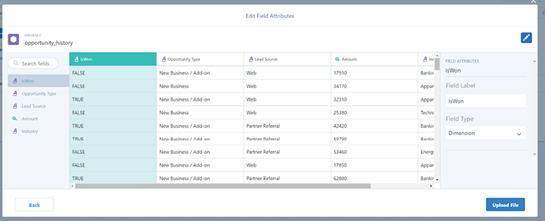
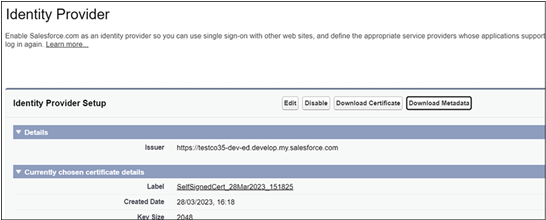
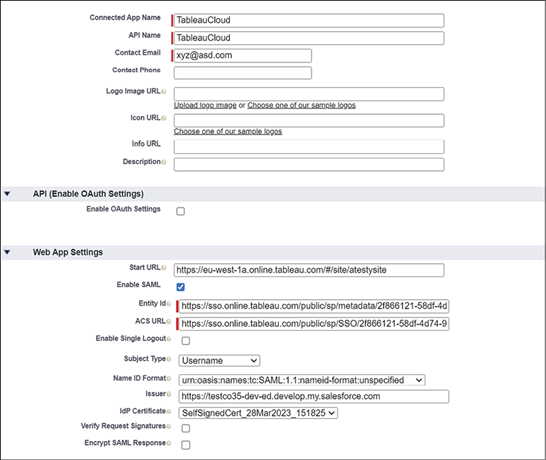
And finally, we explored the full integration of Tableau CRM (previously referred to as CRM Analytics) within the Salesforce platform. This native solution amalgamates Salesforce’s comprehensive sales, service, and marketing data with Tableau’s visualization prowess, allowing businesses to detect trends, anticipate outcomes, identify anomalies, and enhance customer experiences.
In short, the marriage of Salesforce and Tableau is more than just the sum of its parts. It is a potent blend that unlocks the full potential of customer data, empowers users to work more efficiently, and uncovers advanced insights. By leveraging this powerful combination, organizations can make data-driven decisions with greater ease and accuracy, thereby boosting their overall performance. And this is the power of harnessing two world-class solutions to enhance your business’s strategic decision-making capabilities.
More Details