Aug 23, 2024
Using Tableau and Salesforce in practice – Troubleshooting, Tricks, and Best Practices
Now that you have gained a solid understanding of the synergistic power of Salesforce and Tableau, it is time to convert this newfound knowledge into practice. Here are some practical steps to guide you in this exciting journey:
- Think in terms of business needs: Always frame your application of Salesforce and Tableau in terms of what your business needs. Remember, technology should serve your business goals, not the other way around. Begin by identifying key business questions or challenges, then determine how Salesforce and Tableau can help address them.
- Start small and scale: It can be tempting to apply your new knowledge across the entire business straight away. However, it is often beneficial to start small. Choose a specific project or team to pilot your initiatives, then gradually scale based on your successes.
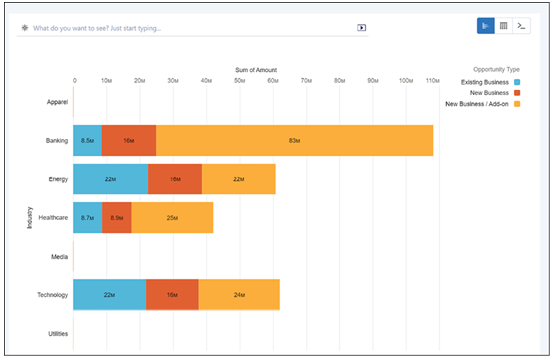
- Practice data visualization: Spend time honing your data visualization skills with Tableau. Data visualization is an art, and just like any art, it improves with practice. Explore different charts and dashboards, play with customization options, and learn what types of visualization best communicate different kinds of information.
- Dive into Salesforce CRM: Make sure to get your hands dirty with Salesforce’s CRM functionalities. It is one thing to understand it theoretically, but experiencing it firsthand will cement your understanding and help you find ways to enhance your organization’s workflows.
- Embrace the power of Einstein AI: Do not shy away from the advanced capabilities offered by Einstein AI. While AI might seem intimidating, remember that Einstein AI models require no coding and can greatly boost your analytic capabilities. Do not hesitate to experiment and explore how AI can benefit your organization.
- Join the community: Salesforce and Tableau have vast, passionate communities full of experts willing to share their experiences and insights. Join forums, participate in webinars, and attend user group meetings. The knowledge and support you can find within these communities is invaluable.
- Iterate and learn from mistakes: You are likely to face challenges as you begin implementing Salesforce and Tableau. Do not be disheartened. Use these challenges as learning opportunities. Adopt a mindset of continuous improvement, adjusting and refining your approach as you progress.
- Stay up-to-date: Salesforce and Tableau are dynamic, evolving platforms. Make sure to stay updated with the latest features and improvements. Regularly check official blogs, attend product webinars, and subscribe to newsletters.
Remember, the journey from learning to practice is a marathon, not a sprint. Be patient with yourself, continue learning, and keep refining your skills. With time, you will become proficient in harnessing the combined power of Salesforce and Tableau to drive your organization forward.
More Details